Definition Components Importance Biology Diagrams
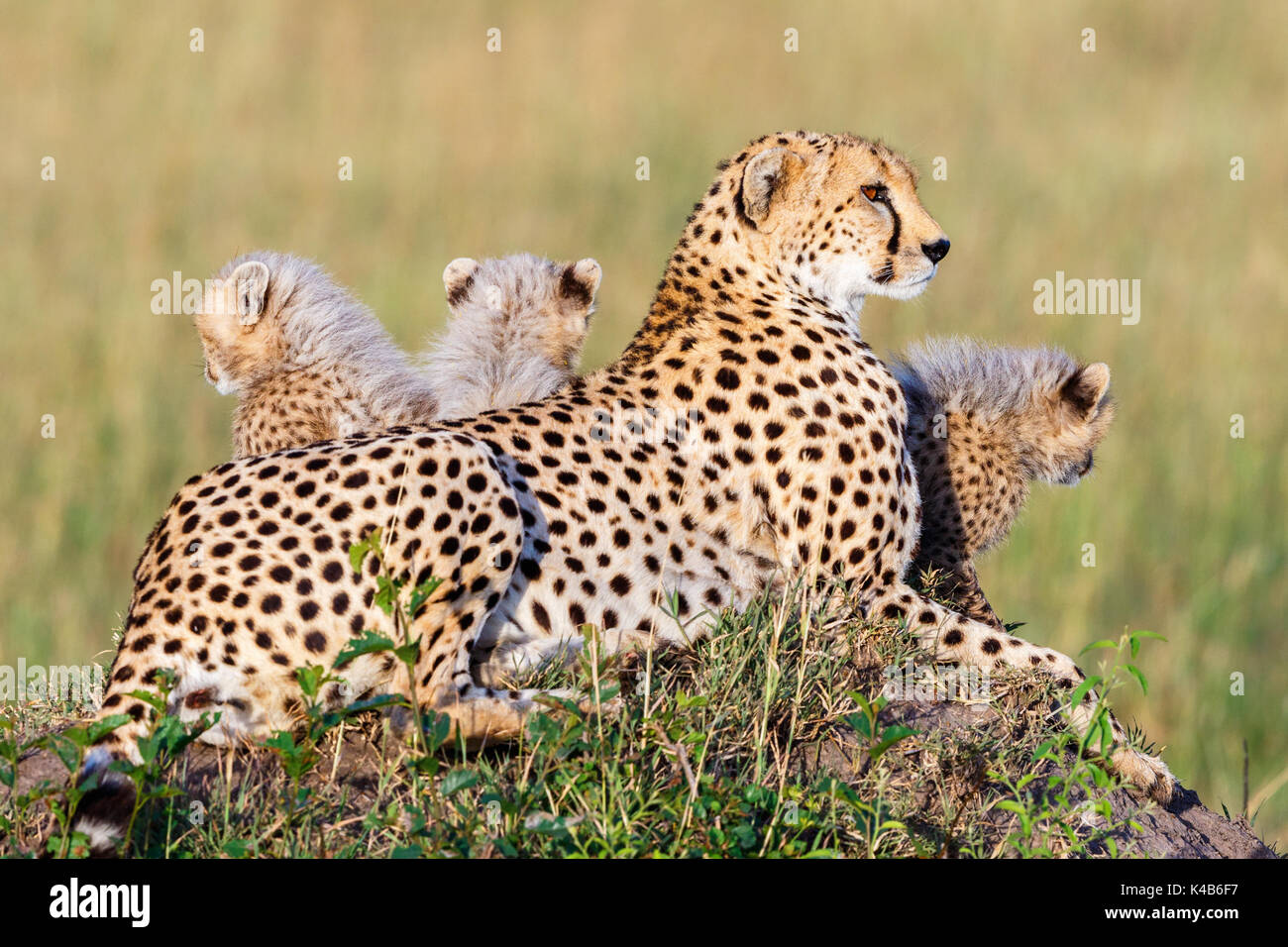
BlogDefinition Components Importance Biology Diagrams Cheetah | Image Source: Natural Habitat Adventures. ⫸ Conclusion. The savanna food web is a marvel of interconnectedness. Every organism plays a crucial role, from the grasses that fuel the grazers to the predators that maintain populations. This delicate balance is vulnerable - changes at one level ripple throughout the system.

Food chains of the savanna. This section is going to be about a three food chains of the savanna Secondary Consumer: The secondary consumers in these food chains are the cheetah, hyena, and the lion. Tertiary Consumer: Teritary consumer in these food chains is the vulture.

Understanding the Cheetah's Role in the Food Chain Biology Diagrams
As you move up the food chain, each level receives only about 10% of the energy from the level below it. This energy loss limits most food chains to 3-4 trophic levels. Savanna food chains follow these same principles as energy transfers between trophic levels, beginning with producers. Savanna Food Chain Trophic Levels and Components Explained
The cheetah is a large species of feline that lives primarily in the grasslands of Africa. Its speed allows it to chase other animals down for food and to avoid predators. The Food Chain ; Resources. American Wildlife Foundation: Cheetah ; Cheetah ; Photo Credits. Joshelerry/iStock/Getty Images. See More Animals. Facts & Information About

Cheetah ecosystem and habitat Biology Diagrams
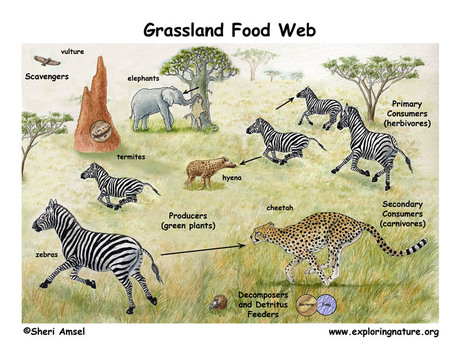
A simplified illustration of the food web of a savanna ecosystem. Every animal species has its role (or niche) in the ecosystem that it lives in. As a carnivorous predator, the cheetah's role in the ecosystem is important as it helps to maintain balanced and healthy food webs. The food chain throughout the African savanna is shown on the left here. Plants and trees are the producers who photosynthesize, creating macromolecules which primary consumers such as zebras, steenbok, or elephants use to gain energy. These are primary consumers are then in turn eaten by secondary consumers such as cheetahs, hyenas or lions.
