Figure 2 from Tumor suppressor mechanisms in immune aging Biology Diagrams
BlogFigure 2 from Tumor suppressor mechanisms in immune aging Biology Diagrams Chief among these factors is the drug retention issue, where paclitaxel has been shown to linger in the tumor cells for a week and is thus able to exert its cytotoxicity longer compared with the newer mitosis-selective inhibitors with a median half-life of approximately 13 h. 35, 64, 65, 66 Additionally, it is likely that quiescent cancer cells

Mitosis is controlled by a network of kinases and phosphatases. We screened a library of small interfering RNAs against a genome-wide set of phosphatases to comprehensively evaluate the role of human phosphatases in mitosis. We found four candidate spindle checkpoint phosphatases, including the tumor suppressor CDKN3.

Genetics, Cancer Cell Cycle Phases Biology Diagrams
The stages of the cell cycle (G1: Gap 1, S: DNA synthesis, G2: Gap 2, and M: mitosis) are indicated. Tumor suppressors act to maintain checkpoints (arrows) whereas oncogenes allow for checkpoints

Mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1/2 (MST1/2) are core tumor suppressors in the Hippo signaling pathway. MST1/2 have been shown to regulate mitotic progression. Here, we report a novel mechanism for phospho-regulation of MST2 in mitosis and its biological significance in cancer. We found that the mi …

Oncogenes, Tumor Suppressor Genes, and DNA Repair Genes Biology Diagrams
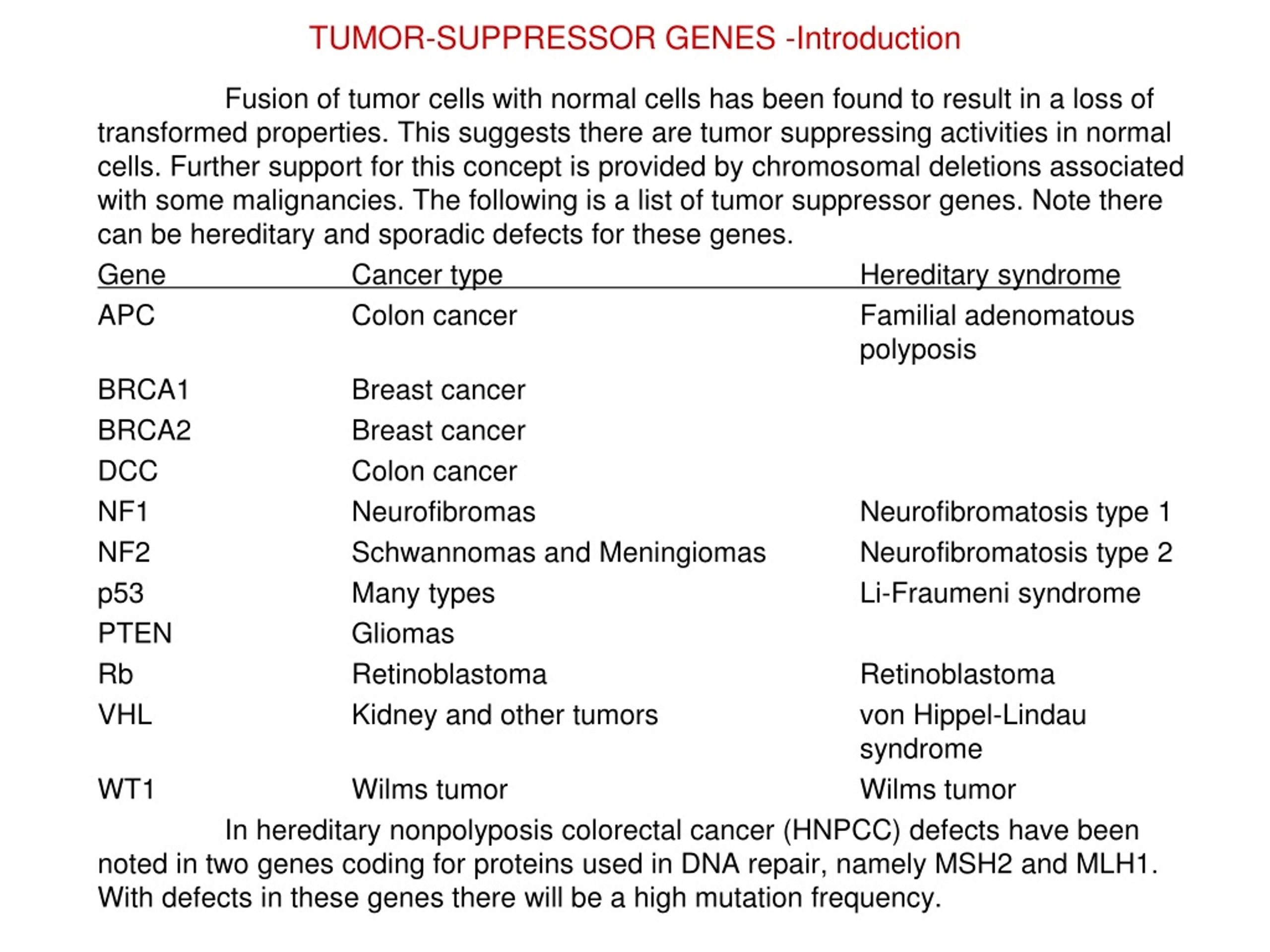
But most tumor suppressor gene mutations are acquired during a person's lifetime, not inherited. For example, TP53 is an important tumor suppressor gene. It codes for the p53 protein, which helps keep cell division under control. Inherited changes in the TP53 gene can lead to Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Family members with this syndrome have an

Mitosis is controlled by a network of kinases and phosphatases. We screened a library of small interfering RNAs against a genome-wide set of phosphatases to comprehensively evaluate the role of human phosphatases in mitosis. We found four candidate spindle checkpoint phosphatases, including the tumor suppressor CDKN3. The interference with cell adhesion results in indirect suppression of cell division due to contact inhibition. It has been observed that a few tumor suppressors may act in cooperation to inhibit cell mitosis 3. Tumor suppressors p15, p16, p18, p19, p21 and p27 inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which, in turn, inhibit Rb 11, 24.